Table Of Content
To address these issues, it created a matrix that could identify those who had made important decisions in the past few years. It then used the matrix to establish clear decision rights and motivators more in tune with the company’s desired goals. Sales directors were made accountable for dealers in their region and were evaluated in terms of the sales performance of those dealers. This encouraged ownership and high performance on both sides, and drew in critically important but previously isolated groups, like the manufacturer’s warranty function.
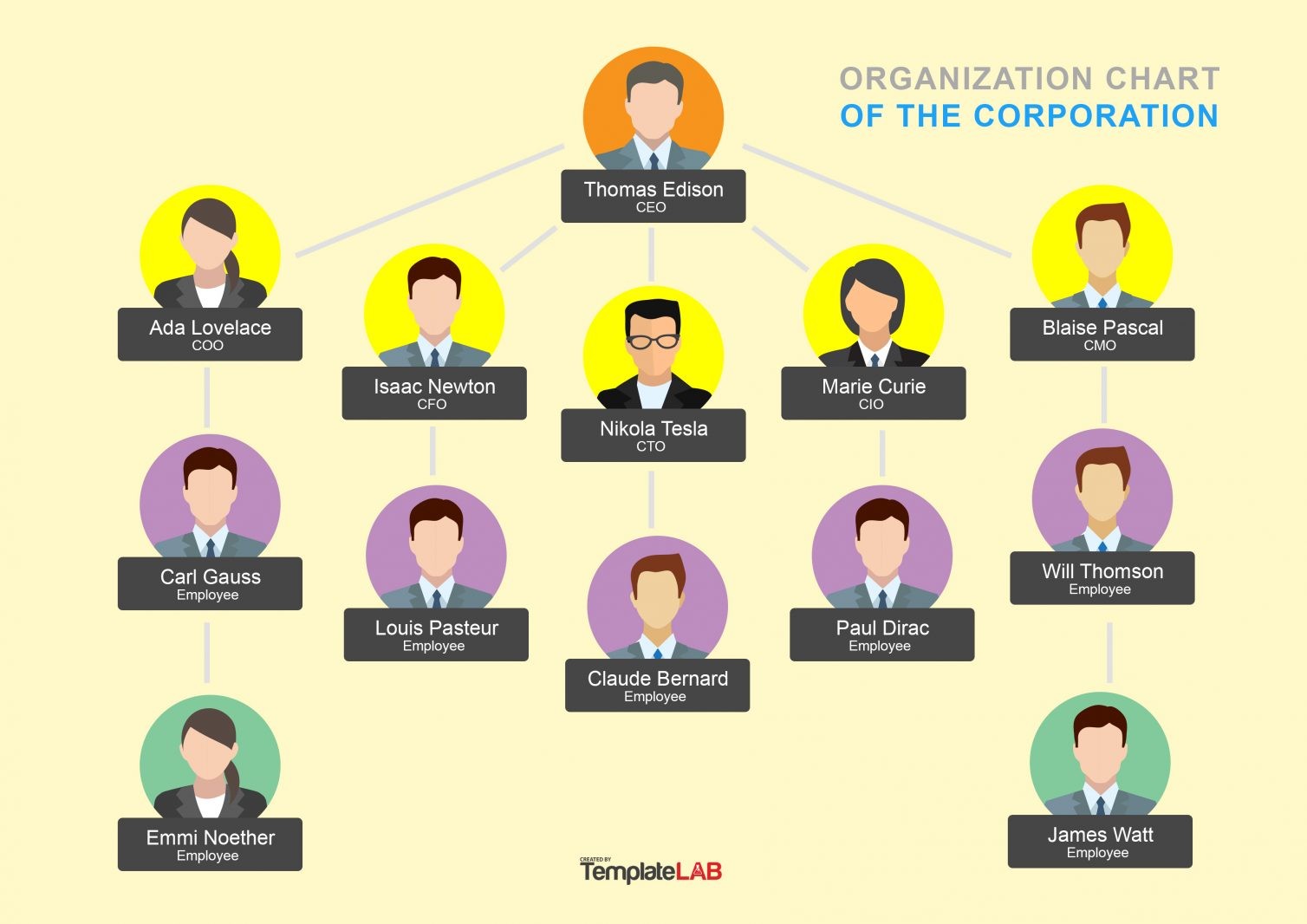
Step five: Organizational chart and roles
Organizational Structure: The Complete Guide To Organizational Structures - FourWeekMBA
Organizational Structure: The Complete Guide To Organizational Structures.
Posted: Tue, 02 Apr 2024 07:00:00 GMT [source]
It’s important to include objective metrics and organisational data in the review. Taking an insight-driven HR approach can provide HR and leaders with objective indicators to reveal how well the organisation is doing and track improvements and also quantify the scale of a problem. This can be used to justify the need for a bigger picture exercise. Over time, developments and practices may reach a point where they are no longer fit with each other or with the strategy that they are trying to implement.
Design of highly functional genome editors by modeling the universe of CRISPR-Cas sequences
If more leaders understood org design, maybe 50% of employees wouldn’t quit because of their manager. Just maybe we could give back the 30% of time that employees say isn’t used productively. Maybe we could erase the lack of diversity in our firms and instill a greater sense of belonging among our teams. Maybe we could save more world-changing companies and technologies from being scaled to death. Our diverse, global teams bring deep industry and functional expertise and a range of perspectives that question the status quo and spark change.
What is the Most Used Organizational Design Framework?
It’s also likely to have a more motivated workforce and be better prepared to weather disruption. Companies such as Apple and Pixar are well known for going far beyond lines and boxes, taking into account questions such as where employees gather in communal spaces and how the organizational context shapes behavior. One small but fast-growing enterprise-software player we know made some minor changes to senior roles and reporting as part of a recent organizational redesign. But the biggest impact came from changing the performance-management system so that the CEO could see which parts of the company were embracing change and which were doing business as usual.
Matrix Organizational Structure
Ogg’s vision is that the organization’s highest priority is to provide the best possible talent wherever the organization creates value. Most of the well-known organization models in use today originated in the 70s and 80s. Their creators were moving organizations from the industrial age hierarchical models to flatter, more responsive structures.
Roles and responsibilities clarify who does what and who is accountable for what. For the staff to adjust their behavior in a more cooperative direction, they need to understand their own responsibilities and those of their colleagues. They also need to know how these responsibilities are to be discharged, what decision rights and key capabilities are needed, and how to measure success.
Business Leaders Face Many Organizational Design Challenges
With 44% of them burning out before they’ve accomplished their objective. The answer to your organizational design conundrum won’t come from a big consulting firm, an analyst, or even from us. Within your team, you already have the intelligence and experience needed to produce the design you need.
This is the polar opposite of the way most businesses approach change and is partly responsible for the much higher success rates seen at Navalent. At the highest level of abstraction — where people are most comfortable — it’s easy to agree to a clear strategy. However, this is by far the least useful level to consider organizational design strategy.
Without full, explicit leadership buy-in, no change initiative can succeed. While these plans look good on paper, they don’t stand up in the real world. And, because all the planning work was done upfront, it’s too late to change anything once implementation begins. You can’t expect to succeed with a benchmarked or ‘template’ approach.
Flat organizations don't rely on an org chart, instead depending on the social connections of individuals to collaborate on specific problems and opportunities. Using the architecture analogy above, if an office building has been developed with several extensions as it has grown, the layout may become ’patchy‘, slowing down communications and leading to ‘silo’ working. This may justify an organisation design–level review of what a new building might look like. They may change their strategy, goals or purpose to align with a new vision for the future.
Our facile coupling of synthesis, characterization, and machine analysis provides powerful tools to quantitate performance parameters accelerating next-generation vehicles for nucleic acid medicines. The third trigger is where organisation design overlaps with organisational development. This is a future-focused organisational re-design, and will often involve a review of the existing operations to identify what can be kept (because it is already aligned) and what needs to be changed or introduced. Wherever it sits, it’s good practice to use multi-disciplinary teams and employee involvement techniques to ensure a wide range of individuals and functions are involved. However, if success in one area is inextricably linked to practice elsewhere, and a variety of mechanisms need re-aligning, then larger-scale organisation design is more appropriate.
Other reasons that prompt organization design includes a change in leadership, strategy or the marketplace in which the organization operates. A 2014 Strategy& survey found that 42 percent of executives felt that their organization was not aligned with the strategy, and that parts of the organization resisted it or didn’t understand it. If that’s a familiar problem in your company, the principles in this article can help you develop an organization design that supports your most distinctive capabilities and supports your strategy more effectively. Constraints on your business — such as regulations, supply shortages, and changes in customer demand — may be out of your control.
Now that we’ve covered the basic principles of organization design, it should be clear that a holistic approach is critical. At the micro level, you must deliberately make trade-offs and mitigate their downsides. At the macro level, you must ensure all decisions are made with the ultimate business strategy. As hard as it may be, leaders must govern this process and be the ultimate decision-makers about what’s best for the business.

No comments:
Post a Comment